By Harold Reiter, posted January 17,
2017 —
Currently,
I have the delightful task of working with twenty high-flying fourth and fifth
graders at Barringer Academic Center in Charlotte, North Carolina, in
partnership with the Advanced Studies Department on topics that include
fractions, integer arithmetic, area, puzzles, and spatial geometry. What the
problems have in common is that they all have an arithmetic entry point, and
they all include something mysterious.
 For
example, to compute the product (a + b)(c
+ d), we could partition a rectangle
of dimensions a + b by c + d into four non-overlapping rectangular
regions and add the areas ac, bc, ad,
and bd. This visual representation—the
area model for multiplication—shows the product of two sums of numbers as the
area of a suitably chosen rectangle. This link between addition and
multiplication is precisely the distribution property of real numbers.
For
example, to compute the product (a + b)(c
+ d), we could partition a rectangle
of dimensions a + b by c + d into four non-overlapping rectangular
regions and add the areas ac, bc, ad,
and bd. This visual representation—the
area model for multiplication—shows the product of two sums of numbers as the
area of a suitably chosen rectangle. This link between addition and
multiplication is precisely the distribution property of real numbers.
To show the versatality of this representation, I asked my students to compute the product of 216 • 23 in vertical format and then the
area of a 23 × 216
rectangle. Finally I challenged them to divide the large rectangle into six
rectangles and find the area of each.
When I asked my students to
build a rectangle that measures 216 × 19 and compute its area, we saw that the
area model works beautifully with negative numbers as just another way to look
at the distribution of multiplication over addition.
Extending
to polynomials, we could point out that when x = 10, the product (2x2 + x + 6)(2x + 3) gives the answer above, 4968. You can tie this to
the place-value idea and point out that polynomial arithmetic is actually
easier than the integer arithmetic because there are no “carries” to worry
about.
A Puzzle
Before you
read the solution, try this puzzle yourself. Even if you make only a little
progress, you’ll see how productive a struggle can be for your students.
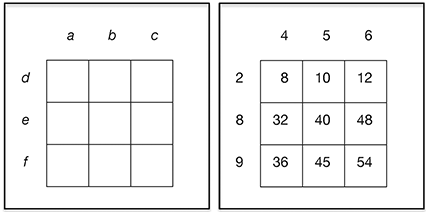
Arrange the numbers 2, 4,
5, 6, 8, and 9 in a 3 × 3 area
model using each digit exactly once. When the multiplication is completed, what
is the largest possible sum obtainable?
Solution: The sum of the
six digits listed is 34. We can view the multiplication table as a rectangular
array of size A × B,
where A is the sum of the entries
along the top and B is the sum of the
entries on the side. For example, if we use a = 4,
b = 5, c = 6, d = 2,
e = 8, and f = 9, then the area of our
rectangle would be (4 + 5 + 6) • (2 + 8 + 9)
= 15 • 19.
The sum of the entries in
the multiplication table is the area of the 15 ×
19 rectangle, which is pretty quickly computed. Each
rectangle you can build from these digits must have height plus width equal to
34. Therefore, if the width is 17 + x, then the height is 17 – x. The product, or area, is 172 – x2.
The
largest possible sum is the largest possible area; that is, 172 – 02
= 289. To be complete, one optimal solution uses 2 + 6 + 9 = 4 + 5 + 9 = 17. Are
there any other ways to achieve the target score of 289?
Ask your
students to show you just their top row of numbers, the a, b, and c. Here’s where the mystery comes in: with
a little practice, you can tell them their sum without even writing any
numbers. Because 17 – (a + b + c) is usually very small, you can compute 289 – (17 – (a + b + c))2
= (a + b + c)(d + e + f ).
A final challenge connects
with the area model in a surprising way. Consider the 6 × 8 grid of 48 unit squares.
- How many squares of any size are bounded by grid lines?
- How many rectangular regions are bounded by grid lines?
To apply
the area model to get the answer to question 2, build the multiplication table
for the numbers 1 through 8 times the numbers 1 through 6, and ask yourself how
many rectangular regions have as a lower right corner the lower right corner of
that square?
 Harold Reiter has taught mathematics for more than fifty-two years. In
recent years, he has enjoyed teaching at summer camps, including Epsilon,
MathPath, and MathZoom. His favorite current activity is teaching fourth and fifth
graders two days each week.
Harold Reiter has taught mathematics for more than fifty-two years. In
recent years, he has enjoyed teaching at summer camps, including Epsilon,
MathPath, and MathZoom. His favorite current activity is teaching fourth and fifth
graders two days each week.